Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
A coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary heart disease.
Every year, 28,000 CABGs are performed in the UK.
Coronary arteries and coronary heart disease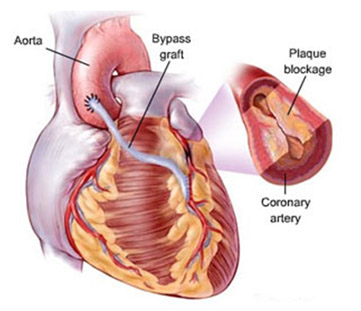
The heart needs a constant supply of blood. This is supplied by two main large blood vessels called the left and right coronary arteries.
Over time, these arteries can become narrowed and hardened by the build-up of fatty deposits called plaques. The narrowing of the arteries is known as atherosclerosis. People with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries are said to have coronary heart disease.
Risk factors for coronary heart disease include:
– Older age
– Smoking
– Obesity
– A high-fat diet
– Strong family history
Coronary heart disease can cause angina, which is chest pain that occurs when the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart becomes restricted.
While many cases of angina can be treated with medication, severe angina may require a CABG to restore the blood supply to the heart .
Another risk associated with coronary heart disease is that one of the plaques in the coronary artery ruptures (splits), creating a blood clot. The blood clot can block the supply of blood to the heart, triggering a heart attack. So, a CABG may also be recommended for people with a high risk of having a heart attack.
The procedure
CABG involves taking a blood vessel from another part of the body, usually the chest or leg, and attaching it to the coronary artery above and below the narrowed area or blockage. This new blood vessel is known as a graft.
The graft diverts the flow of blood around the part of the coronary artery that is narrowed or blocked. Usually, the surgeon will carry out several grafts to make sure the procedure does not have to be repeated in the future. .
Recovery
Recovery after your CABG will take time. Everyone recovers at slightly different speeds. As a rule of thumb, you should be able to sit in a chair after one day, walk after three days and walk upstairs after five or six days.
Outlook
The outlook for people having a CABG is generally good. Most people will experience a significant improvement in symptoms and their heart attack risk will be lowered.
However, it is important to realise that a CABG is not a cure for coronary heart disease. If you do not make lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and quitting smoking, your grafted arteries will eventually also become hardened and narrowed.

